Author: darijungaa
Management Notes
CRISIS HANDLING
Crisis is an unexpected, non-recurring, unplanned, and dramatic problematic situation.
- Organizations have to operate in remote and operating environment. The environment is dynamic which sometimes unfolds to catastrophic & turbulent situations for the organizations, that we call crisis. Crisis is the undesirable and negative situations in the environment that have very much strong impact on the survival, growth and excellence of the organization.
- More specifically, crisis may be caused by changes in technological, socio-cultural, demographic, political-legal, natural, and industry environment in the national and international level.
- Crisis handling strategies should be prepared by the management.
Crisis handling
Followings are the strategies recommended in crisis handling.
- Crisis situation should be solved as soon as possible by the management showing judgment.
- Early warning signals of crisis should be developed, if that is possible. These signals should be continuously monitored to detect the early signals so that they can be handled before they become disastrous. But all crises do not occur with forewarning.
- Adequate authority should be delegated to the lowest level of management in case crisis situation emanates.
- Training to handle crisis situation should be imparted to all levels of management.
- Contingency planning should be formulated to deal with crisis situation. Contingency planning involves developing alternative courses of actions beforehand to deal with crisis situation. Such practices should be rehearsed time and again. It is preparing for the prevention.
- Damage minimization: If crisis becomes unavoidable, attempts should be made to minimize the damage aftermath the crisis.
- Fast recovery aftermath crisis: Managers should help organizations recover the aftermath of crisis as quickly as possible.
- Organizational learning: Once crisis is over, the organization should learn from the crisis, i.e. learning from the past mistakes.
- Crisis team may be built beforehand to deal with crisis situation. Such team should include experts experienced in crisis handling.
External experts may be approached for their help in crisis handling.
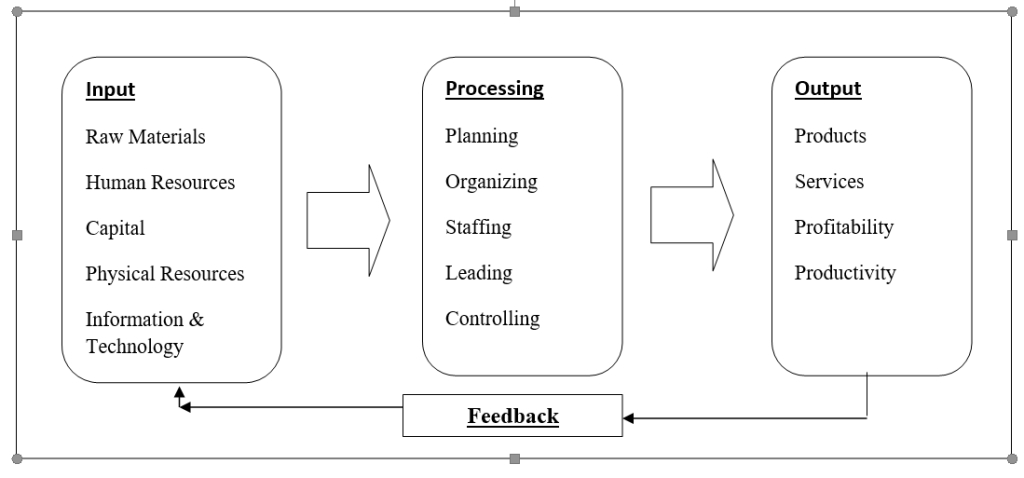
Quantitative Tools for Decision Making
Operations Research Tool
They are used to solve problems that already exist. They aim to optimize by allocating scare resources in the most profitable way. They take system-wide approach and quantify all the variables of the problem. These techniques are suitable for programmed decisions.
- Queuing Models : They are used to control various sorts of waiting lines.
- Game theory: It predicts how rational people will behave in competitive situations.
- Inventory Model: It helps to determine how much inventory to maintain. The model analyzes the various consequences and selects the optimal size of inventory.
- Transportation Model: It helps to determine where various quantities of products must go and the most cost-efficient way to get them there.
- Payoff Matrix
It is a statistical technique. It depicts the probable value of outcomes of each of the decision alternatives. A probability is the degree of likelihood that a particular event will occur.
The expected value of an alternative course of action is computed. It is the sum of the values of all the predicted outcomes of the alternatives multiplied by their respective probabilities.
- Decision Tree
It is a graphical representation of the sequence of decisions required in determining the expected values of alternatives in a payoff matrix.
- Simulation
It is abstraction of reality. It is useful when several uncertain variables affect outcomes. Computers are used to stimulate what will happen to an operation over a time if certain variables are changed.
- Accounting Tools
Breakeven Analysis: It identifies break-even point of neither profit nor loss.
Ratio Analysis: They show relationships between figures for evaluating financial performance. They are used for making efficiency and profitability decisions.
Budgetary Control: It compares actual expenditure with budgeted expenditure. Decisions are made to correct budget variance.
Standard Costing: It is used for making decisions concerning control of unit cost. Standard cost is set for each unit.
Decision Making
Decision-making is the process of identifying and selecting the best course of action for achieving certain goals, i.e. solving a specific problem or exploiting opportunity.
- Decision making is the selection of a particular course of action chosen by the decision maker as the most effective means at his disposal for achieving the goal or goals he is currently emphasizing or for solving the problem.
- In other words, it is choosing a particular course of action from several alternative courses of action for achieving a desired result. In short, it is the choice made by the decision maker about what should or should not be done in a given situation.
- Decision-making is the pervasive process (i.e. essence of management), i.e. used in organizing, leading, controlling, yet it is the core of planning.
Communication
Communication
“Communication is the process of transmitting information from one person to another.”
“Effective communication is the process of sending a message in such a way that the message received is as close in meaning as possible to the message intended.”
Communication is pervasive/basic part of management. Communication is needed in planning, organizing, leading, and controlling.
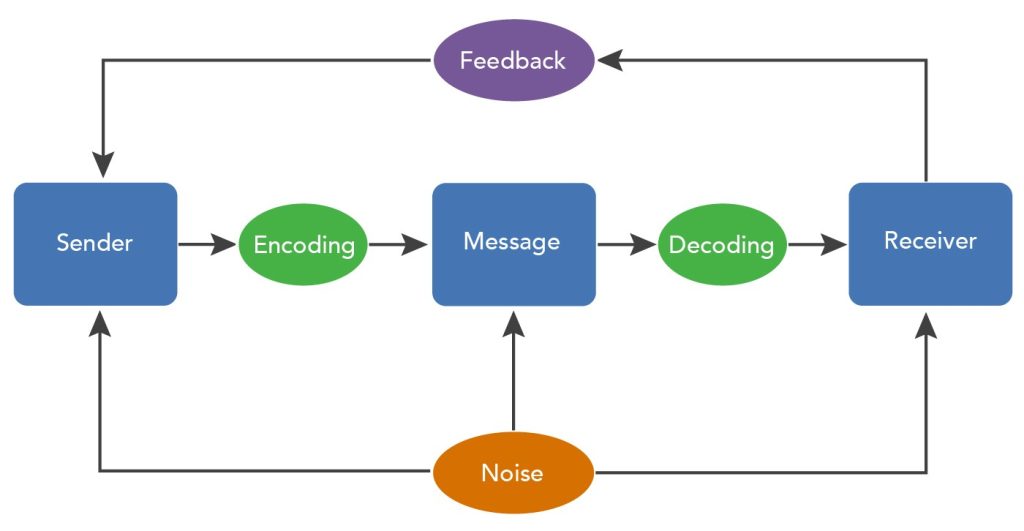
COMMUNICATION PROCESS
“Communication process consists of the steps between a source and a receiver that result in the transference and understanding of meaning” -Stephenson P. Robbins (2001)
Management Theories
MEANING AND DEFINITION OF MANAGEMENT
Management is the process by which a co-operative group directs action towards a common goal. Joseph Messie
To manage is to forecast and plan, to organize, to command, to coordinate and to control. Henry Fayol
“Management is a distinct process consisting of planning, organizing, activation, and controlling, performed to determine and accomplish the objectives by the use of people and resources.” –George R. Terry
Management is the art of knowing what you want men to do in the cheapest way. F.W. Taylor
FEATURES (OR CHARACTERISTICS) OF MANAGEMENT
Management is an activity concerned with guiding human and physical resources such that organizational goals can be achieved. Nature of management can be highlighted as —
- Management is Goal-Oriented: The success of any management activity is accessed by its achievement of the predetermined goals or objective. Management is a purposeful activity. It is a tool which helps use of human & physical resources to fulfill the pre-determined goals. For example, the goal of an enterprise is maximum consumer satisfaction by producing quality goods and at reasonable prices. This can be achieved by employing efficient persons and making better use of scarce resources.
- Management integrates Human, Physical and Financial Resources: In an organization, human beings work with non-human resources like machines. Materials, financial assets, buildings etc. Management integrates human efforts to those resources. It brings harmony among the human, physical and financial resources.
- Management is Continuous: Management is an ongoing process. It involves continuous handling of problems and issues. It is concerned with identifying the problem and taking appropriate steps to solve it. E.g. the target of a company is maximum production. For achieving this target various policies have to be framed but this is not the end. Marketing and Advertising is also to be done. For this policies have to be again framed. Hence this is an ongoing process.
- Management is all Pervasive: Management is required in all types of organizations whether it is political, social, cultural or business because it helps and directs various efforts towards a definite purpose. Thus clubs, hospitals, political parties, colleges, hospitals, business firms all require management. When ever more than one person is engaged in working for a common goal, management is necessary. Whether it is a small business firm which may be engaged in trading or a large firm like Tata Iron & Steel, management is required everywhere irrespective of size or type of activity.
- Management is a Group Activity: Management is very much less concerned with individual’s efforts. It is more concerned with groups. It involves the use of group effort to achieve predetermined goal of management of ABC & Co. is good refers to a group of persons managing the enterprise.
FUNCTIONS (SCOPE) OF MANAGEMENT
Management has been described as a social process involving responsibility for economical and effective planning & regulation of operation of an enterprise in the fulfillment of given purposes. It is a dynamic process consisting of various elements and activities. These activities are different from operative functions like marketing, finance, purchase etc. Rather these activities are common to each and every manger irrespective of his level or status.
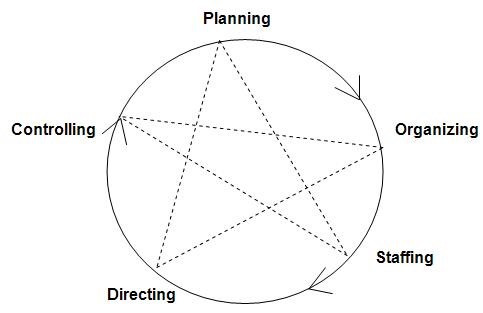
According to Henry Fayol, “To manage is to forecast and plan, to organize, to command, & to control”. Whereas Luther Gullick has given a keyword ’POSDCORB’ where P stands for Planning, O for Organizing, S for Staffing, D for Directing, Co for Co-ordination, R for reporting & B for Budgeting. But the most widely accepted are functions of management given by KOONTZ and O’DONNEL i.e. Planning, Organizing, Staffing, Directing and Controlling.
For theoretical purposes, it may be convenient to separate the function of management but practically these functions are overlapping in nature i.e. they are highly inseparable. Each function blends into the other & each affects the performance of others.
Planning
It is the basic function of management. It deals with chalking out a future course of action & deciding in advance the most appropriate course of actions for achievement of pre-determined goals. According to KOONTZ, “Planning is deciding in advance – what to do, when to do & how to do. It bridges the gap from where we are & where we want to be”. A plan is a future course of actions. It is an exercise in problem solving & decision making. Planning is determination of courses of action to achieve desired goals. Thus, planning is a systematic thinking about ways & means for accomplishment of pre-determined goals. Planning is necessary to ensure proper utilization of human & non-human resources. It is all pervasive, it is an intellectual activity and it also helps in avoiding confusion, uncertainties, risks, wastages etc.
Organizing
It is the process of bringing together physical, financial and human resources and developing productive relationship amongst them for achievement of organizational goals. According to Henry Fayol, “To organize a business is to provide it with everything useful or its functioning i.e. raw material, tools, capital and personnel’s”. To organize a business involves determining & providing human and non-human resources to the organizational structure. Organizing as a process involves:
- Identification of activities.
- Classification of grouping of activities.
- Assignment of duties.
- Delegation of authority and creation of responsibility.
- Coordinating authority and responsibility relationships.
Staffing
It is the function of manning the organization structure and keeping it manned. Staffing has assumed greater importance in the recent years due to advancement of technology, increase in size of business, complexity of human behavior etc. The main purpose o staffing is to put right man on right job i.e. square pegs in square holes and round pegs in round holes. According to Koontz & O’Donnell, “Managerial function of staffing involves manning the organization structure through proper and effective selection, appraisal & development of personnel to fill the roles designed un the structure”. Staffing involves:
- Manpower Planning (estimating man power in terms of searching, choose the person and giving the right place).
- Recruitment, selection & placement.
- Training & development.
- Remuneration.
- Performance appraisal.
- Promotions & transfer.
Directing
It is that part of managerial function which actuates the organizational methods to work efficiently for achievement of organizational purposes. It is considered life-spark of the enterprise which sets it in motion the action of people because planning, organizing and staffing are the mere preparations for doing the work. Direction is that inert-personnel aspect of management which deals directly with influencing, guiding, supervising, motivating sub-ordinate for the achievement of organizational goals. Direction has following elements:
- Supervision
- Motivation
- Leadership
- Communication
- Supervision- implies overseeing the work of subordinates by their superiors. It is the act of watching & directing work & workers.
- Motivation- means inspiring, stimulating or encouraging the sub-ordinates with zeal to work. Positive, negative, monetary, non-monetary incentives may be used for this purpose.
- Leadership- may be defined as a process by which manager guides and influences the work of subordinates in desired direction.
- Communications- is the process of passing information, experience, opinion etc from one person to another. It is a bridge of understanding.
Controlling
It implies measurement of accomplishment against the standards and correction of deviation if any to ensure achievement of organizational goals. The purpose of controlling is to ensure that everything occurs in conformities with the standards. An efficient system of control helps to predict deviations before they actually occur. According to Theo Haimann, “Controlling is the process of checking whether or not proper progress is being made towards the objectives and goals and acting if necessary, to correct any deviation”. According to Koontz & O’Donnell “Controlling is the measurement & correction of performance activities of subordinates in order to make sure that the enterprise objectives and plans desired to obtain them as being accomplished”. Therefore controlling has following steps:
- Establishment of standard performance.
- Measurement of actual performance.
- Comparison of actual performance with the standards and finding out deviation if any.
- Corrective action.
Management System